Thread processing is a method of processing various internal and external threads with thread processing tools.
1. Thread cutting
Generally refers to the method of machining threads on a workpiece with a forming tool or an abrasive tool, mainly including turning, milling, tapping, threading grinding, grinding, and whirlwind cutting. When turning, milling and grinding threads, every time the workpiece rotates, the transmission chain of the machine tool ensures that the turning tool, milling cutter or grinding wheel moves accurately and evenly along the axis of the workpiece by one lead.
When tapping or threading, the tool (tap or die) rotates relative to the workpiece, and the first formed thread groove guides the tool (or workpiece) to move axially.
2. Thread turning
The pitch accuracy of ordinary lathes for turning trapezoidal threads can generally only reach 8-9 (JB2886-81, the same below); processing threads on specialized threading lathes can significantly improve productivity or accuracy.
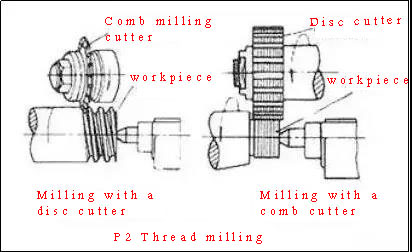
The pitch accuracy of thread milling can generally reach 8 to 9, and the surface roughness is R5 to 0.63 microns. This method is suitable for mass production of general precision threaded workpieces or rough machining before grinding.
4, thread grinding
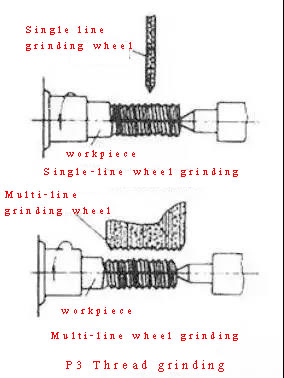 It is mainly used for processing precision threads of hardened workpieces on thread grinders. According to the different cross-sectional shapes of the grinding wheels, it can be divided into single-line grinding wheels and multi-line grinding wheels. The pitch accuracy that can be achieved by single-line grinding wheel grinding is 5 to 6, and the surface roughness is R1.25 to 0.08 microns, and the grinding wheel dressing is more convenient. This method is suitable for grinding precision lead screws, thread gauges, worms, small batches of threaded workpieces and relieving precision hobs.
It is mainly used for processing precision threads of hardened workpieces on thread grinders. According to the different cross-sectional shapes of the grinding wheels, it can be divided into single-line grinding wheels and multi-line grinding wheels. The pitch accuracy that can be achieved by single-line grinding wheel grinding is 5 to 6, and the surface roughness is R1.25 to 0.08 microns, and the grinding wheel dressing is more convenient. This method is suitable for grinding precision lead screws, thread gauges, worms, small batches of threaded workpieces and relieving precision hobs.Multi-line grinding wheel grinding is divided into two types: longitudinal grinding method and plunge grinding method. The width of the grinding wheel of the longitudinal grinding method is smaller than the length of the thread to be ground, and the thread can be ground to the final size by moving the grinding wheel one or several strokes in the longitudinal direction. The width of the grinding wheel of the plunge grinding method is greater than the length of the thread to be ground. The grinding wheel cuts into the surface of the workpiece radially, and the workpiece can be ground after about 1.25 revolutions. The productivity is higher, but the accuracy is slightly lower, and the dressing of the grinding wheel is more complicated. The plunge grinding method is suitable for relieving large batches of taps and grinding certain fastening threads.
5, thread grinding
Use softer materials such as cast iron to make nut-type or screw-type thread grinds, and perform forward and reverse rotation grinding on the parts of the machined threads with pitch errors on the workpiece to improve the pitch accuracy. Hardened internal threads are usually ground to eliminate deformation and improve accuracy.
6, tapping and threading
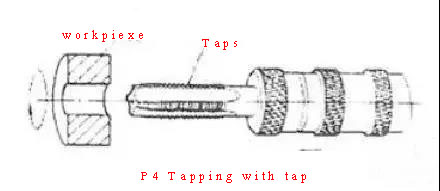 Tapping is to use a certain torque to screw the tap into the pre-drilled bottom hole on the workpiece to process the internal thread.
Tapping is to use a certain torque to screw the tap into the pre-drilled bottom hole on the workpiece to process the internal thread.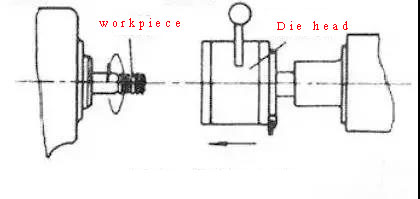 Threading is to use a die to cut an external thread on a bar (or pipe) workpiece. The processing accuracy of tapping or threading depends on the accuracy of the tap or die. Although there are many methods for processing internal and external threads, small diameter internal threads can only be processed by taps. Tapping and threading can be operated manually, and can also be used with lathes, drilling machines, tapping machines and threading machines.
Threading is to use a die to cut an external thread on a bar (or pipe) workpiece. The processing accuracy of tapping or threading depends on the accuracy of the tap or die. Although there are many methods for processing internal and external threads, small diameter internal threads can only be processed by taps. Tapping and threading can be operated manually, and can also be used with lathes, drilling machines, tapping machines and threading machines.Seven, thread rolling
The processing method of plastically deforming the workpiece with a forming rolling die to obtain a thread. Thread rolling is generally performed on a thread rolling machine or an automatic lathe with an automatic opening and closing thread rolling head. It is suitable for mass production standards. External threads of fasteners and other threaded connections.
The outer diameter of the rolled thread is generally no more than 25 mm, the length is no more than 100 mm, and the thread accuracy can reach level 2 (GB197-63). The diameter of the blank used is roughly the same as the pitch diameter of the thread being machined. Rolling generally cannot process internal threads, but for softer workpieces, non-slot extrusion taps can be used to cold extrude internal threads (the maximum diameter can reach about 30 mm). The working principle is similar to tapping. When cold-extruding internal threads, the required torque is about twice as large as that of tapping, and the machining accuracy and surface quality are slightly higher than that of tapping.
▌The advantages of thread rolling are:
①Surface roughness is less than turning, milling and grinding;
②The thread surface after rolling can improve the strength and hardness due to cold work hardening;
③High material utilization rate;
④The productivity is doubled compared with cutting processing, and it is easy to realize automation;
⑤The rolling die has a long life. However, rolling thread requires that the hardness of the workpiece material does not exceed HRC40; the requirement for the dimensional accuracy of the blank is relatively high; the precision and hardness requirements for the rolling die are also high, and it is difficult to manufacture the mold; it is not suitable for rolling threads with asymmetric teeth.
▌According to different rolling molds, thread rolling can be divided into thread rolling and thread rolling.
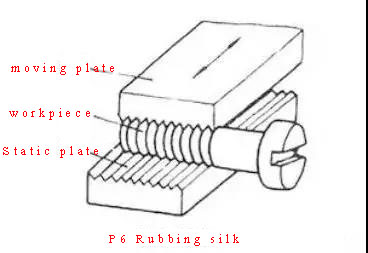
>>> Thread rolling is the arrangement of two thread rolling plates with thread profile staggered by 1/2 pitch. The static plate is fixed, and the moving plate makes a reciprocating linear motion parallel to the static plate. When the workpiece is fed between the two plates, the movable plate advances and rubs the workpiece to plastically deform its surface into a thread.
>>> There are three types of thread rolling: radial thread rolling, tangential thread rolling and rolling head thread rolling.
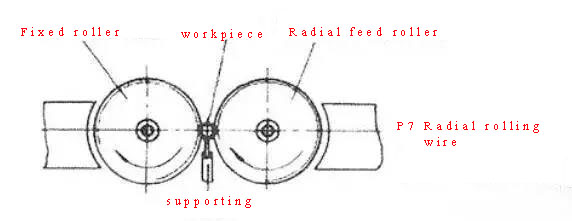
①Radial thread rolling: 2 (or 3) thread rolling wheels with thread profile are installed on mutually parallel shafts, the workpiece is placed on the support between the two wheels, and the two wheels rotate in the same direction at the same speed, one of them The wheel also makes a radial feed movement. The workpiece rotates under the drive of the thread rolling wheel, and the surface is compressed radially to form a thread. For some lead screws with low precision requirements, similar methods can also be used to roll forming.
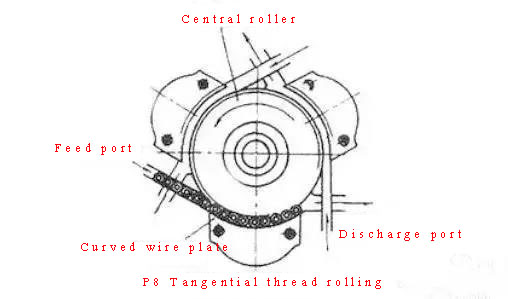
② Tangential thread rolling: also known as planetary thread rolling, the rolling tool consists of a rotating central thread rolling wheel and 3 fixed arc wire plates. During thread rolling, the workpiece can be fed continuously, so the productivity is higher than thread rolling and radial thread rolling.
③Thread rolling head: It is carried out on an automatic lathe, and is generally used to process short threads on the workpiece. There are 3 to 4 thread rolling wheels evenly distributed on the outer circumference of the workpiece in the rolling head. During thread rolling, the workpiece rotates and the rolling head feeds axially to roll the workpiece out of the thread.
Post time: Apr-27-2021